Appearance
redux 的实现
1、createStore
得到数据集合 store
let store = createStore(reducer);
- store
- getState //获取最新的状态
- dispatch //派发 action,payload 去到 reducer
- subscribe
subscribe
react 项目中,在 componentWillMount 中开始监听传入的函数,放进数组 listeners 中, 在 dispatch=>action 后,经过 reducer 得到新的 state 后,执行这个监听的函数
subscribe 函数会返回一个解除监听的函数
在 componentWillUnmount 的是时候取消监听 this.unsubscribe();
js
//创建仓库
const createStore = (reducer) => {
// console.log(reducer)
//状态
let state;
//监听函数数组
let listeners = [];
//getState用来获取最新的状态
let getState = () => state;
//向仓库派发action,
let dispatch = (action) => {
//传入老的state,action,经过reducer处理得到新的state
state = reducer(state, action);
listeners.forEach((listener) => listener());
};
//订阅仓库内的状态变化事件,当状态发生变化之后会调用对应的监听函数
//订阅方法执行后会返回一个取消订阅的函数,调用它会取消订阅
let subscribe = (listener) => {
listeners.push(listener);
return () => {
listeners.filter((l) => listener !== l);
};
};
dispatch();
return {
getState, //获取最新的状态对象
subscribe, //原来订阅状态变化事件
dispatch,
};
};
export { createStore };
2、示例:单个组件,单个 reducer 的处理方式
counter.js
js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { createStore } from './../redux/redux';
//action type
const ADD = 'ADD';
const MINUS = 'MINUS';
//state 是状态树,可以是任意的结构
//action是个纯对象,类型和payload {type:'ADD',amount:2}
let reducer = (state = { number: 0 }, action) => {
if (action === undefined) return state;
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD':
return { number: state.number + action.amount };
case 'MINUS':
return { number: state.number - action.amount };
default:
return state;
}
};
//现在是有一个store ,如果是有多个处理组件使用redux,就要有多个store,我们只需要一个,这是个问题,需要合并成一个store
let store = createStore(reducer);
//add方法,minus方法就称为action creator
function add(amount) {
return { type: 'ADD', amount };
}
function minus(amount) {
return { type: 'MINUS', amount };
}
class Counter extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
//用仓库里的初始状态来初始化组件的内部本地状态
this.state = { number: store.getState().number };
}
componentWillMount() {
//订阅
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({ number: store.getState().number });
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
//取消订阅
this.unsubscribe();
}
handleAdd = () => {
// store.dispatch({type:ADD,amount:2})
//换成action creater
store.dispatch(add(2));
};
handleMin = () => {
//store.dispatch({type:MINUS,amount:2})
//换成action creater
store.dispatch(minus(2));
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.handleAdd}>+</button>
<span>{this.state.number}</span>
<button onClick={this.handleMin}>-</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Counter;
todo.js
js
import React from 'react';
import { createStore } from './../redux/redux';
const ADD_TODO = 'ADD_TODO';
const DEL_TODO = 'DEL_TODO';
let addTodo = (text) => {
// action creator
return { type: ADD_TODO, text };
};
let delTodo = (index) => {
// action creator
return { type: DEL_TODO, index };
};
//1.创建reducer 一般的状态都会初始化成一个对象
let initState = { list: ['请输入...'] };
let reducer = (state = initState, action) => {
if (action === undefined) return state;
switch (
action.type //判断动作的类型
) {
case ADD_TODO: //如果要增加一个todo的话
//!!! 永远不要修改原来的状态,每次都要生成一个新的状态
// {type:'ADD_TODO',text:'study'}
return { list: [...state.list, action.text] };
case DEL_TODO:
// {type:'DEL_TODO',index:1}
return {
list: state.list.filter((item, index) => index !== action.index),
};
default:
return state;
}
};
//2.创建store
let store = createStore(reducer);
//3. 创建Todo组件
//4.连接store和Todo组件
class Todo extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
//这时其实是实现了store的状态和本地状态的映射
//仓库里状态很多,但是本组件可能只需很少一部分,那么只需要把自己需要的部分拿过来即可
this.state = { list: store.getState().list };
}
componentWillMount() {
store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({ list: store.getState().list });
});
}
handleKeyDown = (event) => {
//取得当前按下的键
let keyCode = event.keyCode;
if (keyCode === 13) {
//获取输入框的值
let text = event.target.value;
store.dispatch(addTodo(text)); //向仓库派发一个action
event.target.value = '';
}
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type="text" onKeyDown={this.handleKeyDown} />
<ul>
{this.state.list.map((item, index) => (
<li key={index}>
{item}{' '}
<button onClick={() => store.dispatch(delTodo(index))}>x</button>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Todo;
这种有相同的东西可以去合并,action types 可以抽离出来,他们每个 reducer 都会产生各自的 state, 写一个公用方法返回他们各自的新的 state
3、combineReducers 的第一步
在 redux 文件下,创建 types.js,写 action types
创建 reducers 文件夹,把 counter,todo 里的 reducer 放在这里,并创建 index.js,用来合并 counter,todo 这两个 reducer
js
//现在是有一个store ,如果是有多个处理组件使用redux,就要有多个store,我们只需要一个,这是个问题,需要合并成一个store
import { createStore } from '../redux';
/*要合并个各reducer处理过的state合并到一个store
* 旧状态 {number:0} {list:[]}
* 新状态 {counter:{number:0},todo:{list:[]}}
* */
import counter from './counter';
import todo from './todo';
let combineReducers = (reducers) => (
state = { counter: { number: 0 }, todo: { list: [] } },
action,
) => {
//返回一个reducer
let newState = {};
if (action === undefined) return state;
for (var key in reducers) {
newState[key] = reducers[key](state[key], action);
}
return newState;
};
let reducer = combineReducers({
counter,
todo,
});
let store = createStore(reducer);
export default store;
4、combineReducers 的第二步,
在 redux 文件加下新建 combineReducers.js
单个 reducer 就是为了产出 state,多个的话在函数内部定义一个空对象,找到每个 reducer 处理返回新的 newState
js
let combineReducers = (reducers) => (state = {}, action) => {
//返回一个reducer
let newState = {};
for (var key in reducers) {
newState[key] = reducers[key](state[key], action);
}
return newState;
};
export default combineReducers;
- reducers 文件夹
- counter 的 reducer
- todo 的 reducer
- index 入口
在 index 中引入 combineReducers,合并 counter 和 todo 的 reducer
js
import combineReducers from './../combineReducers';
/*要合并个各reducer处理过的state合并到一个store
* 旧状态 {number:0} {list:[]}
* 新状态 {counter:{number:0},todo:{list:[]}}
* */
import counter from './counter';
import todo from './todo';
let reducer = combineReducers({
counter,
todo,
});
export default reducer;
5、connect
counter,todo 组件中公用的部分
如果在创建个 counter2 组件,下面的代码在组件重复写,下面要处理这种,抽出公用的部分
js
constructor() {
super();
//用仓库里的初始状态来初始化组件的内部本地状态
this.state = {number: store.getState().counter.number};
}
componentWillMount() {
//订阅
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({number: store.getState().counter.number});
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
//取消订阅
this.unsubscribe();
}
js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { ADD, MINUS } from './../redux/types';
import store from './../redux/reducers';
class counter2 extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log(props);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => this.props.add(2)}>+</button>
<span>{this.props.value}</span>
<button onClick={() => this.props.minus(3)}>-</button>
</div>
);
}
}
let connect = (mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) => (WrapComponent) => {
class Proxy extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = mapStateToProps(store.getState());
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log(store);
//订阅
store.subscribe(() => {
this.unsubscribe = this.setState(mapStateToProps(store.getState()));
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
//取消订阅
this.unsubscribe();
}
render() {
return (
<WrapComponent
{...this.state}
{...mapDispatchToProps(store.dispatch)}
/>
);
}
}
return Proxy;
};
//mapStateToProps 把store里的状态对象映射成属性
let mapStateToProps = (state) => ({
value: state.counter.number,
});
//把dispatch方法映射成ui组件的属性
let mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
add: (amount) => dispatch({ type: ADD, amount }),
minus: (amount) => dispatch({ type: MINUS, amount }),
});
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(counter2);
可以把 connect 抽离出来,在 redux 下创建 connect.js 文件,
connect 返回一个高级组件,把最新的 state,dispatch 传给子组件,通用处理
6、Provider
现在 store 是各自独立的,我们应该把 store 放在顶层组件,通过 context api 实现,子组件都可以 从 store 中获取最新的 state
那么可以在入口文件包裹一个顶层组件 Provider组件,
js
<Provider store={store}>
<App/>
</Provider>,
js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { PropTypes } from 'prop-types';
class Provider extends Component {
//通过context的api处理
getChildContext() {
return { store: this.props.store };
}
render() {
return this.props.children;
}
}
Provider.childContextTypes = {
store: PropTypes.object,
};
export default Provider;
js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { PropTypes } from 'prop-types';
let connect = (mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) => (WrapComponent) => {
class Proxy extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {};
}
componentWillMount() {
//订阅
this.context.store.subscribe(() => {
this.unsubscribe = this.setState(
mapStateToProps(this.context.store.getState()),
);
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
//取消订阅
this.unsubscribe();
}
render() {
return (
<WrapComponent
{...this.state}
{...mapDispatchToProps(this.context.store.dispatch)}
/>
);
}
}
//connect 通过 context 获取store
Proxy.contextTypes = {
store: PropTypes.object,
};
return Proxy;
};
export default connect;
7、applyMiddleware
为什么 dispatch 需要 middleware? 正常的流程
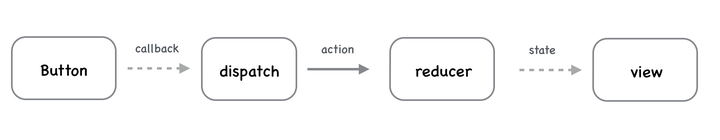
js
store.dispatch({type:'ADD',Amount:1})
//正常流程是dispatch直接派发一个action,如果想隔三秒在派发的话
store.dispatch(setTimeout(()=>{type:'ADD',Amount:1}},3000))
//看到dispatch 只能接收一个action,对于函数这种,要处理下,这就用到了中间件
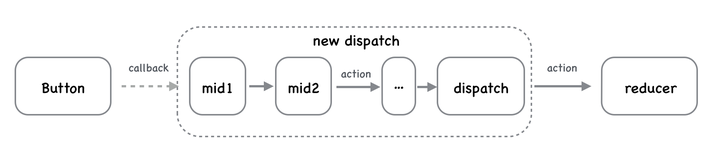
经过中间件重新返回一个新的 dispatch action 到 reducer
middleware 怎么写?
先看个柯里化的例子比较好理解下面的中间件写法
把 func1 传给 func2,又把 func2 传给 func3
先写个例子:记录 dispatch 前后 state 变化日志的列子
js
let logger = (store) => (next) => (action) => {};
//也就是下面的
var logger = function logger(store) {
return function (next) {
return function (action) {};
};
};
//使用的话传入logger
//中间件的一般是柯里化,返回一个函数在传入另一个函数
let store = applyMiddleware(logger)(createStore)(reducer);
middleware 的写法理解
js
//middleware 就是传入的logger,
//let store=applyMiddleware(logger)(createStore) 传入了createStore,
//就是redux中的createStore,createStor又是传入的reducer
let applyMiddleware = middleware=>{ //middleware就看做是logger
return createStore=>reducer=>{
//这是之前原始的createStore方法,createStore传入了reducer
let store=createStore; //得到原始的store
//记住middleware就看做是logger,logger=store=>next=>action=>下面的意思就是把
//store传入了middleware中间件logger
middleware=middleware(store)
//此时得到了next函数 middleware
//next函数 middleware又传入store.dispatch既是action,返回一个新的dispatch
let dispatch = middleware(store.dispatch)
//最后返回 store 和新的dispatch
return {...store, dispatch}
}
}
//简化下也就是下面写的
let applyMiddleware = middleware =>createStore => reducer => {
let store = createStore(reducer);
middleware = middleware(store)
let dispatch = middleware(store.dispatch)
return {...store, dispatch}
}